Batch processing vs real-time processing in machine learning workflows
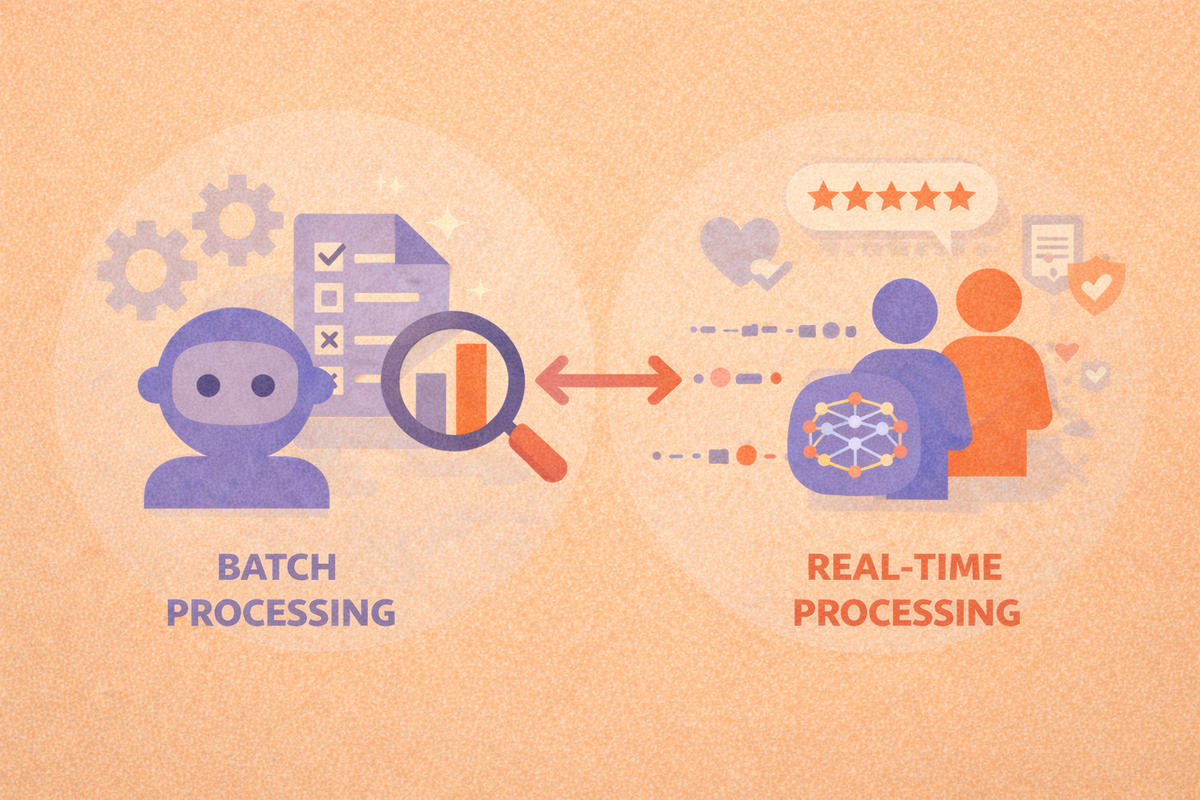
About batch processing
Batch processing in machine learning refers to running models on large volumes of data at scheduled intervals rather than continuously. Data is collected over a period of time, processed together, and then used to generate outputs such as predictions, reports, or scores.
Batch workflows are common in use cases like forecasting, periodic risk scoring, reporting, and offline analysis. They are well suited to situations where decisions do not need to be made immediately and where stability and cost efficiency are priorities.
One of the main advantages of batch processing is reproducibility. Because inputs are fixed for each run, it is easier to compare results across model versions and track performance changes over time. Batch jobs are also simpler to test and debug, since failures tend to be deterministic rather than timing-dependent.
Batch processing does have limitations. Outputs can become stale if underlying data changes rapidly. If a decision needs to reflect the most recent information, waiting for the next batch run may be unacceptable. Batch workflows also struggle with interactive use cases, where users expect immediate responses.
In practice, batch processing is often the default starting point for machine learning teams because it is easier to reason about and scale predictably.
About real-time processing
Real-time processing evaluates or runs machine learning models continuously as new data arrives. Instead of waiting for scheduled jobs, models respond immediately to events, user actions, or streaming data.
Real-time workflows are used when latency matters. Examples include fraud detection, personalization, alerting systems, and any application where delayed decisions reduce value or increase risk. In these settings, speed and consistency under load are as important as correctness.
The strength of real-time processing is responsiveness. Models operate on the most current data available, enabling systems to adapt quickly to changing conditions. This can significantly improve user experience and decision quality.
However, real-time workflows are more complex. They must handle unpredictable traffic, partial failures, and timing-related issues. Testing and evaluation are also harder, since inputs are continuously changing and results can vary depending on context.
Real-time systems require careful design to balance accuracy, latency, and reliability. Without proper safeguards, small errors can propagate quickly.
Comparison
| Dimension | Batch processing | Real-time processing |
| Decision timing | Scheduled | Immediate |
| Data input | Collected over time | Continuous |
| Primary strength | Stability and efficiency | Responsiveness |
| Complexity | Lower | Higher |
| Reproducibility | High | Lower |
| Cost optimization | Easier | More constrained |
| Typical failure | Stale outputs | Missed or delayed responses |
| Best-fit use cases | Reporting, forecasting, offline scoring | Fraud detection, alerts, personalization |
Suggestion
When choosing between batch and real-time processing, start with the decision requirements rather than the technology. If decisions can tolerate delay, batch processing is usually simpler, cheaper, and easier to evaluate. If decisions must reflect the latest data, real-time processing may be necessary despite its complexity.
Many teams adopt a hybrid approach. Batch pipelines handle core analysis and periodic scoring, while real-time pipelines address high-impact, time-sensitive events. This combination often delivers the best balance between reliability and responsiveness.
Conclusion
Batch and real-time processing are not competing solutions so much as complementary tools. Batch processing provides consistency and control; real-time processing delivers immediacy. Understanding when each is appropriate helps teams build machine learning workflows that are both effective and sustainable.
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions
Is batch processing outdated compared to real-time systems?
No. Batch processing is still widely used because it is simpler, more cost-efficient, and easier to evaluate and debug. Many production ML systems rely primarily on batch workflows.
When is real-time processing truly necessary?
Real-time processing is needed when decisions must reflect the most recent data and delays meaningfully reduce value or increase risk, such as fraud detection or user-facing personalization.
Can a system use both batch and real-time processing?
Yes. Many teams use batch pipelines for periodic analysis and real-time pipelines for time-sensitive decisions.
Which approach is easier to evaluate and test?
Batch processing is generally easier to evaluate because inputs are fixed and results are reproducible. Real-time systems require more careful monitoring and experimentation.
What’s the biggest risk of choosing the wrong approach?
Using batch when real-time is required can lead to stale decisions, while using real-time unnecessarily can introduce avoidable complexity and reliability risks.