Supervised LLM Fine-Tuning
This template is designed for you to get started with the process of supervised LLM fine-tuning.
The goal of supervised LLM fine-tuning is to optimize your large language model (LLM) to generate responses given user-defined prompts which are more context specific than the original foundation model.
There are multiple scenarios where you might want to use this approach:
- Document classification
- General Question-Answering (QA) systems
- Information Retrieval
- Customer Support services
Normally the need for this dataset collection template arise when you want:
- train the large foundation model to follow your instructions;
- create any Natural Language Processing (NLP) type of model, such as Sentiment Analysis, Text Summarization, Question-Answering, Named-entity recognition tailored to your domain;
- fix the model’s mistakes in the generated responses;
- generate responses in a specific style;
- switching from few-shot model generation scenario to the zero-shot learning mode, without a need to provide any examples;
- reduce model generation costs.
All these tasks require a dataset of prompts and corresponding responses, or completions, for example:
[
{
"prompt": "<prompt text>",
"response": "<generated response>"
},
{
"prompt": "<prompt text>",
"response": "<generated response>"
},
{
"prompt": "<prompt text>",
"response": "<generated response>"
}
]How to collect the dataset
Start your project with collecting initial set of prompts:
[
{
"prompt": "<prompt text>"
},
{
"prompt": "<prompt text>"
},
{
"prompt": "<prompt text>"
}
]Each JSON item will be rendered as a separate task in Label Studio to complete the response.
Starting your labeling project
Need a hand getting started with Label Studio? Check out our Zero to One Tutorial.
- Create new project in Label Studio
- Go to Settings > Labeling Interface > Browse Templates > Generative AI > Supervised LLM Fine-tuning
- Save Alternatively, you can create a new project by using our Python SDK:
import label_studio_sdk
ls = label_studio_sdk.Client('YOUR_LABEL_STUDIO_URL', 'YOUR_API_KEY')
project = ls.create_project(title='Chatbot Model Assessment', label_config='<View>...</View>')Import the dataset
Using the Python SDK you can import the dataset with input prompts into Label Studio. With the PROJECT_ID of the project
you’ve just created, run the following code:
from label_studio_sdk import Client
ls = Client(url='<YOUR-LABEL-STUDIO-URL>', api_key='<YOUR-API_KEY>')
project = ls.get_project(id=PROJECT_ID)
project.import_tasks('prompts.json')Then you can start annotating the dataset by creating the responses.
Export the dataset
There have to be from hundreds to thousands of tasks labeled to get your LLM being fine-tuned, depending on the complexity of your problem statement.
After you’ve labeled enough tasks, you can export the dataset in the following raw Label Studio JSON format:
[
{
"id": 1,
"data": {
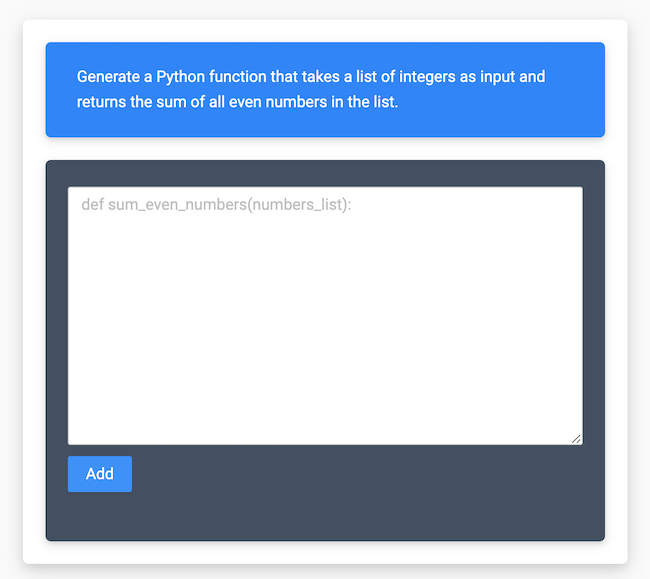
"prompt": "Generate a Python function that takes a list of integers as input and returns the sum of all even numbers in the list."
},
"annotations": [
{
"id": 1,
"created_at": "2021-03-03T14:00:00.000000Z",
"result": [
{
"from_name": "instruction",
"to_name": "prompt",
"type": "textarea",
"value": {
"text": [
"def sum_even_numbers(numbers):\n return sum([n for n in numbers if n % 2 == 0])"
]
}
}
],
// other fieldsIt represents the list of tasks with annotations. Each task has a data.prompt field with the input prompt, and each “annotations” item contains a response result under result.value.text field.
You can create more than one annotation per task.
Alternatively, you can download the same data in CSV format:
prompt,instruction
"Generate...","def sum..."How to configure the labeling interface
The Supervised Language Model Fine-tuning template includes the following labeling interface in XML format:
<View className="root">
<Style>
<!-- Different CSS styles for the prompt and the answer input -->
</Style>
<View className="container">
<View className="prompt">
<Text name="prompt" value="$prompt"/>
</View>
<View className="answer-input">
<TextArea name="instruction" toName="prompt"
maxSubmissions="1" required="true"
requiredMessage="You must provide the response to the prompt"
placeholder="Type your answer here..."
rows="10"
/>
</View>
</View>
</View>Here it takes input prompt in "$prompt" variable and renders it as a text block with a blue background defined
by <Style> section Then it renders a text area with a black background to collect the response from the annotator. The
response is saved in "$instruction" variable.
You can modify "prompt" in XML comments to see how it looks with your data.
How to fine-tune the model
You generated examples can be used to finetune the opensource LLM models like LLaMa, Pythia, Falcon, StableLM, MPT, etc. You can check the complete list of models on HuggingFace LLM leaderboard, download and finetune the model from Model Hub. Alternatively, there are finetuning services available: OpenAI, CoHere, MosaicML, Google Cloud AI Platform, AzureML, etc.